Diagnostic Accuracy and Complication Rates of Fusion Images Created Using Real-Time Ultrasound with CT for Identification of Peripheral Lung Lesions in Patients Undergoing Biopsy
Several investigators have described the
utility and safety of ultrasound (US)-guided transthoracic cutting needle
biopsy and fine needle aspiration in chest lesions. However, these studies were
conducted only in the conventional B mode, and thus occurrence of mis-targeting
is possible.
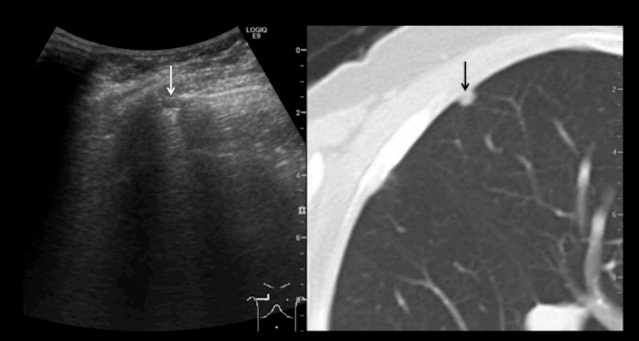
Recently, fusion
image with real-time US and computed tomography (CT) has been introduced in
interventional radiology. In the chest, fusion image can be used to assist in
detecting the pleural-lesion contact area in extremely small solid nodules.
Moreover, the fusion image of the pleural membrane associated with solid
component of part-solid ground-glass nodule (GGN), results in localization of
the lesion.
In this paper, the
authors described the clinical benefit of US-guided lung biopsy using fusion
image and aimed to retrospectively compare the diagnostic accuracy and
complication rates of US-guided lung biopsy with B-mode alone and those of a
fusion image created using real-time US and computed tomography (CT).
This retrospective
study was conducted at a single institution. Between September, 2013 and
September, 2016, 50 peripheral lung lesions in 50 patients (40 males, 10
females; median, 74 years old) were performed by US-guided percutaneous cutting
needle biopsy using the B-mode alone or fusion image. Final diagnoses were
based on surgical outcomes or clinical follow-up results for at least 12 months
after biopsy. To assess prebiopsy characteristics, all lesions were divided
into two groups: group 1 (identification on B-mode) and group 2 (identification
on fusion image).
The results showed
that of 50 peripheral lesions, 40 lesions (80%) were detected by means of
B-mode alone (group 1), and 10 lesions (20%) were identified by fusion image
(group 2). The diagnostic accuracy of group 1 was 90% (36/40 lesions), and the
diagnostic accuracy of group 2 was 100% (10/10 lesions). Nodule type and the
size of the lesions showed significant group wise differences (p < 0.001 and
p = 0.02, respectively). Pneumothorax occurred immediately after the first
puncture in five of 50 (10%) lesions, with no symptom development in all
patients.
In conclusion, fusion
images created using real-time US and CT may be useful for identification of
the minimal size of potential target lung lesions and may be more suitable for
improved yields with US-guided lung biopsy.
Article by Rinpei
Imamine, et al, from Japan.
Full access: http://t.cn/Etflv59
评论
发表评论